Vespa! Cloud Infrastructure for Search Applications!
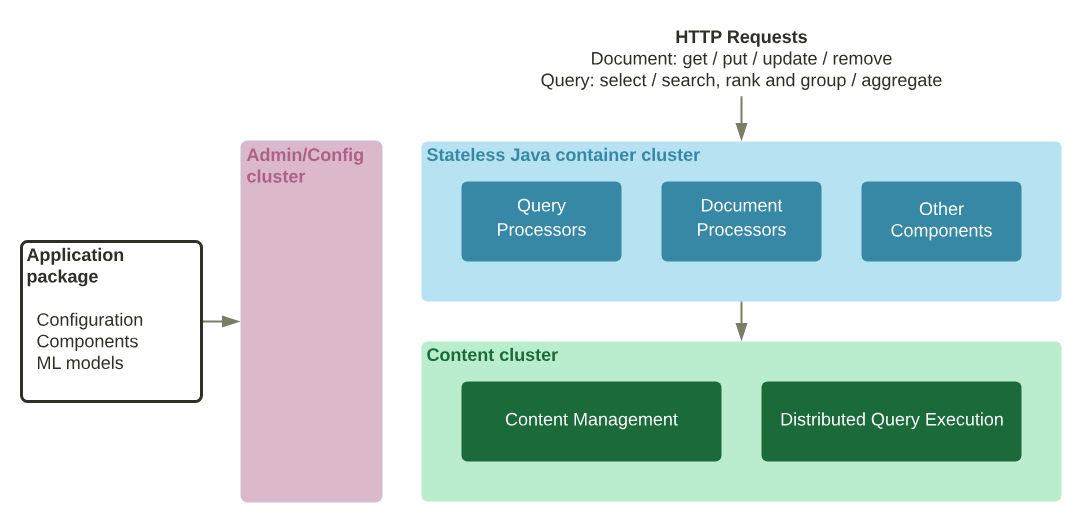
Multi-node Vespa on GKE! Vector + Keyword ranking! Autoscaling Search, Document Processing, and Content Replication!
Config servers (3)Content nodes (2)Query containers (2)Feed containers (2)Admin node (1)
Started locally on Docker → migrated to GKE using Vespa’s tutorials
Vespa in Production
Why Vespa
Vespa is one of the most mature and performant vector-aware search engines in production today — originally developed at Yahoo and now powering AI search at scale for global companies. It natively combines text and vector retrieval, supports streaming writes, online re-ranking, and large-scale low-latency inference in a single platform.
- Trusted by Yahoo, Perplexity, Vinted, FARFETCH, Onyx (Danswer Cloud), Splore.
- Combines ANN (approximate nearest neighbor) retrieval with BM25 keyword ranking, dynamic filtering, and tensor computation for real-time personalization.
- Designed for multi-node scaling — horizontal sharding, coverage tracking, and replica rebalancing are built into the serving layer.
- Fully open-source and Kubernetes-ready, with deep documentation at docs.vespa.ai.
Vector + Keyword HybridStreaming WritesRe-ranking PipelinesOn-cluster ML InferenceHorizontal ScalingOpen Source
Tip: Keep ANN profiles separated by embedding dimension (384 vs 1536) to avoid input shape mix-ups.
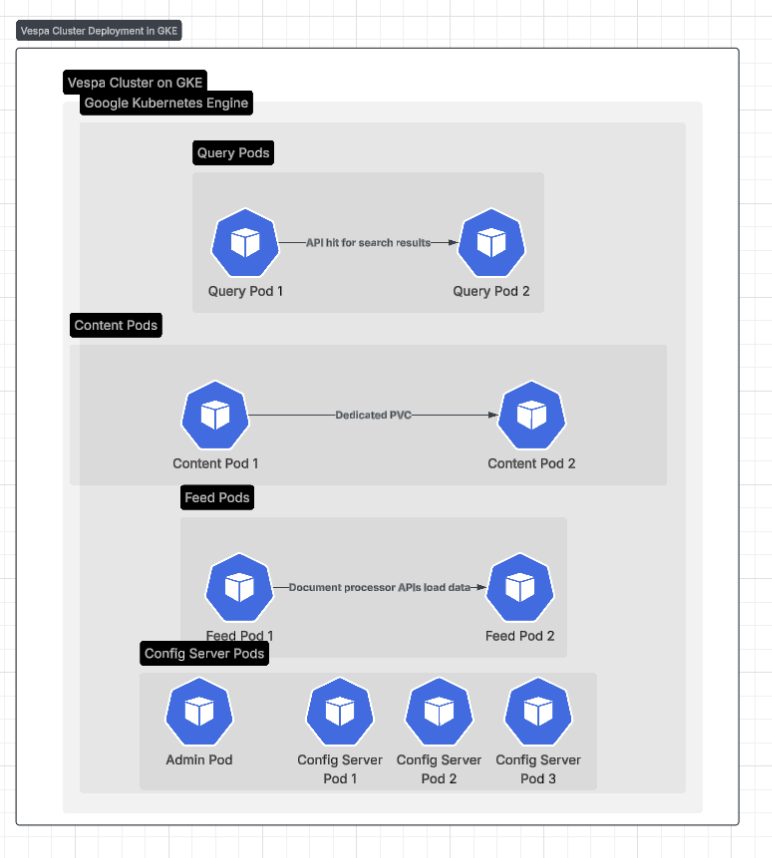
Cluster Diagram
Cluster Topology (Kubernetes view)
Control plane (Config/Admin) · Data plane (Stateless/Content) · Services (LB/Headless) · PVCs · Ports & health
Diagrams: Vespa cluster roles and concrete GKE deployment — config/admin (control plane), content (stateful), and query/feed (stateless). Headless internal svc
vespa-internal; edge via vespa-query and vespa-feed at :8080.Schema Explorer
Schema & Rank Profiles
schema arxiv2 {
document arxiv2 {
field arxiv_id type string { indexing: attribute | summary; fast-search: true }
field title type string { indexing: index | summary; match: bm25 }
field abstract type string { indexing: index | summary; match: bm25 }
field categories type array<string> { indexing: attribute | summary; fast-search: true }
field family type string { indexing: attribute | summary; fast-search: true }
field title_Embedding_1 type tensor<bfloat16>(d0[384]) {
indexing: attribute
attribute: fast-search
distance-metric: angular
}
field Summarized_Abstract_Embedding_1 type tensor<bfloat16>(d0[384]) {
indexing: attribute
attribute: fast-search
distance-metric: angular
}
}
fieldset default { fields: title, abstract }
rank-profile keyword inherits default {
first-phase { expression: bm25(title) + bm25(abstract) }
}
rank-profile ann_title_1 inherits default {
inputs { query(query_embedding) tensor<bfloat16>(d0[384]) }
first-phase { expression: closeness(title_Embedding_1, query_embedding) }
}
rank-profile ann_summary_1 inherits default {
inputs { query(query_embedding) tensor<bfloat16>(d0[384]) }
first-phase { expression: closeness(Summarized_Abstract_Embedding_1, query_embedding) }
}
rank-profile ann_multi_1 inherits default {
inputs {
query(query_embedding) tensor<bfloat16>(d0[384])
query(w_title) double
query(w_abs) double
}
first-phase {
expression: query(w_title) * closeness(title_Embedding_1, query_embedding)
+ query(w_abs) * closeness(Summarized_Abstract_Embedding_1, query_embedding)
}
}
# Fine-tune style profile example
rank-profile ann_fine_tune_1 inherits default {
inputs { query(query_embedding) tensor<bfloat16>(d0[384]) }
first-phase {
expression: closeness(title_Embedding_1, query_embedding) +
pow(max(0, closeness(Summarized_Abstract_Embedding_1, query_embedding)), attribute(weight1)) * attribute(weight2)
}
}
}Highlights
bm25ontitleandabstractfor lexical recall.fast-searchattributes onarxiv_id,categories,family.- Multiple bf16 vector fields (384-d) with angular distance.
- Multi-vector fusion (
ann_multi_1) with query-time weights. - Fine-tune variant (
ann_fine_tune_1) with attribute-based boost.
Quick Checks
- After feeding a doc,
GET /document/v1/arxiv2/arxiv2/docid/<id>should return it. - Using ANN profiles? Provide
input.query(query_embedding)with shape 384. - Keep 384-dim vs 1536-dim profiles separate to avoid shape mix-ups.
Scaling & Monitoring
Scaling & Latency (observed)
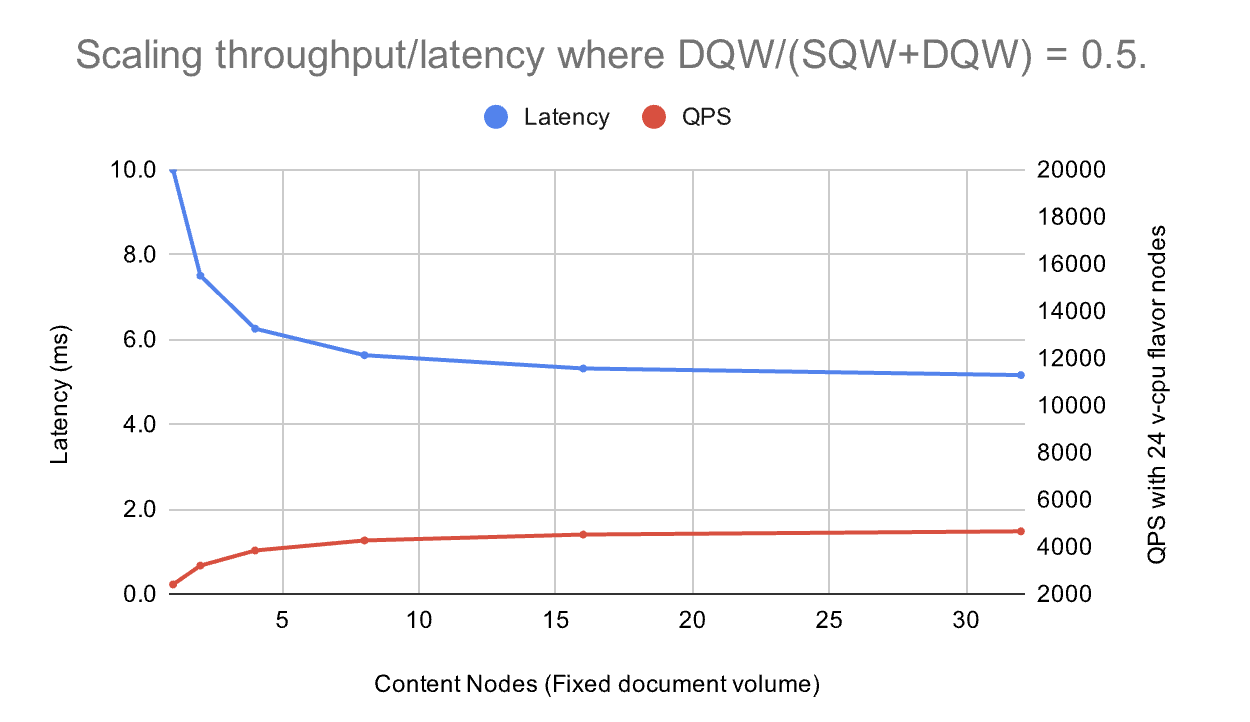
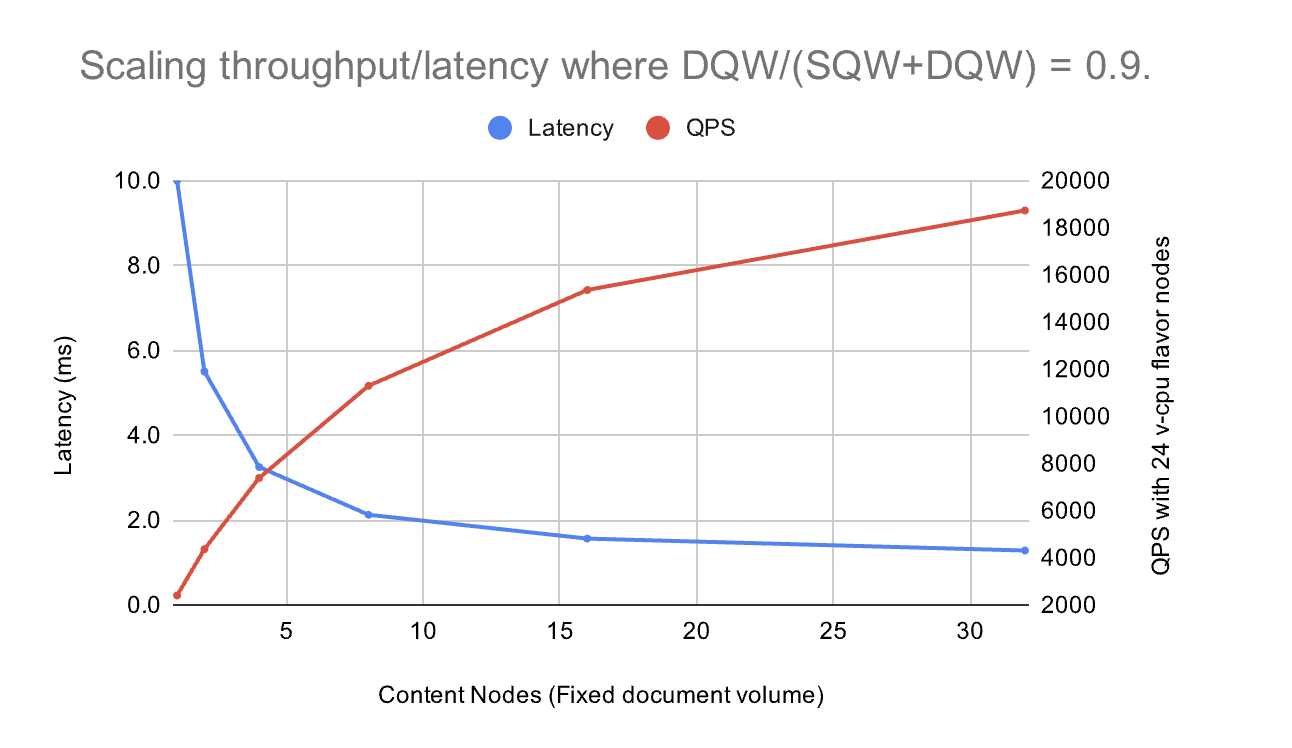
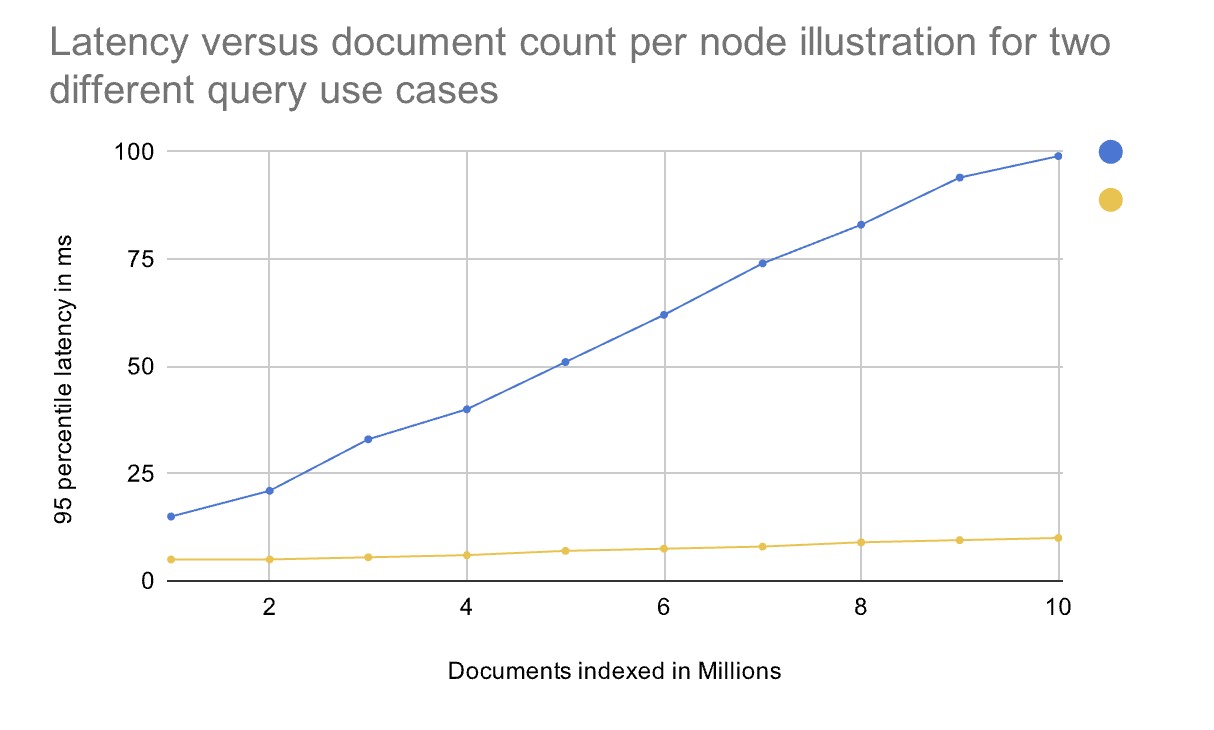
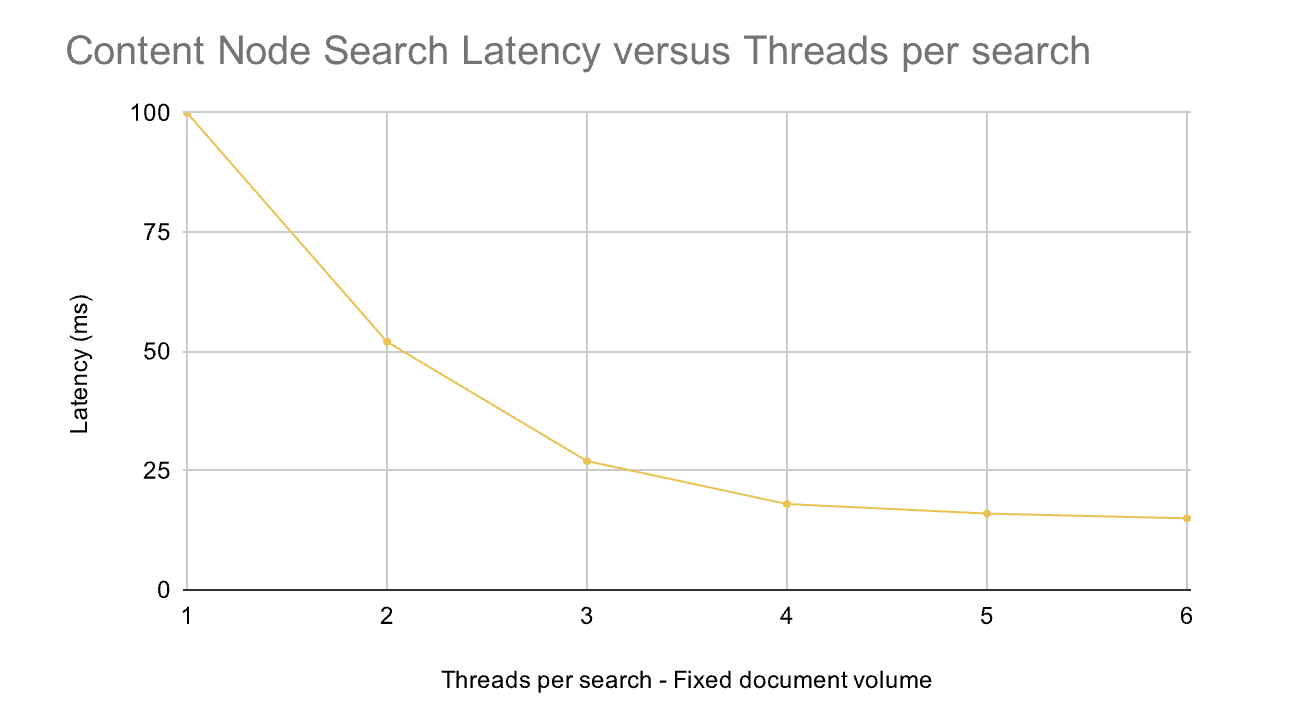
Scaling
- Horizontal: increase replicas for
vespa-queryandvespa-feedto raise QPS/ingest. - Vertical: grow container resources and content memory if paging/latency spikes.
- Autobalancing: content cluster rebalances buckets after scale; brief <100% coverage is normal.
Monitoring
Pod health
cfg-0
configserver · ● up
cfg-1
configserver · ● up
cfg-2
configserver · ● up
content-0
content · ● up
content-1
content · ● up
query-0
query · ● up
query-1
query · ● up
feed-0
feed · ● up
feed-1
feed · ● up
Refreshed 8:35:30 PM
K8s resource snapshot
- admin: 1 Gi
- content (each): 1 Gi
- query (each): 1.5 Gi
- feed (each): 1.5 Gi
Hook Prometheus/Grafana for p95/99 latency, feed throughput, disk usage.
Research & Bench Notes
Premium Vespa Features
- Multi-vector search & fusion: rank profiles can combine several embeddings (e.g., title + abstract) with query-time weights.
- Tensor expression language: closeness/dot products, feature mixing, and custom first-phase/second-phase ranking on-cluster.
- On-cluster ML inference: run models alongside serving for low-latency re-ranking and personalization.
- True hybrid retrieval: ANN + BM25 + filters in a single query plan with coverage/degradation reporting.
- Streaming writes & consistency: online ingest while maintaining search availability and bucket rebalancing.
- Schema-driven performance: fast-search attributes, typed tensors (incl.
bfloat16), and per-field distance metrics. - Rich filtering/YQL: structured predicates with facets, ranges, and joins without leaving the serving tier.
The Evaluation Stack Part I: Auto Labeler
Using AI to generate relevance labels for search evaluation.
0:00 / 0:00